HTC One M8 Review > Performance: The Qualcomm Snapdragon 801
Performance: The Qualcomm Snapdragon 801
ARM hardware partners are moving at an ever-rapid pace, seemingly releasing a new, faster bit every few months. At MWC 2014, which ended just over a calendar month ago, popular ARM hardware vendor Qualcomm released their latest loftier-end SoC – the Snapdragon 801 – to tide us over until the Snapdragon 810 and 64-bit chips are set. This SoC is what you'll discover within the HTC One M8 and other Android flagships launching at the outset of 2014.
If you're thinking that the Snapdragon 801 isn't a huge step over the Snapdragon 800, you'd exist right. The 801 expands on the foundation laid with the 800 by packing the same quad-cadre Krait 400 CPU, the aforementioned Adreno 330 GPU, and the same 32-bit dual-channel LPDDR3 retention controller. Clock speeds for all these items have increased, merely the effects of this shouldn't be massive.

However, nosotros are talking about an upgrade to the HTC One M7, which was announced in February 2013 and powered by the Snapdragon 600. When we started to run across the get-go wave of Snapdragon 800 devices later in the year at that place was a sizable performance gap between the two SoCs, so I'm expecting to see something similar going from the M7 to the M8.
Interestingly, there are two variants of the HTC 1 (M8) in the wild: the international version, which packs the Snapdragon 801 MSM8974ABv3 clocked at 2.26 GHz, and the Asian model with a Snapdragon 801 MSM8974ACv3 clocked at two.45 GHz. HTC kindly provided me with the latter model, which should be even faster than the Snapdragon 800 and give more meat to this operation department.
Yous'll also notice the GPU clock speed has been raised to 578 MHz, and the LPDDR3 memory controller now clocked at 933 MHz for 14.nine GB/s of bandwidth. Every bit far as I'k aware, eMMC 5.0 is not utilized on the all new HTC One. You lot can compare the device to the HTC One M7 and the Snapdragon 800-powered Nexus 5 in the table below.
| Specs | HTC One (M8) | Google Nexus 5 | HTC One (M7) |
| SoC | Snapdragon 801 MSM8974ACv3 | Snapdragon 800 MSM8974AA | Snapdragon 600 APQ8064 |
| CPU | 4x Krait 400 @ 2.45 GHz | 4x Krait 400 @ two.26 GHz | 4x Krait 300 @ 1.seven GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 330 @ 578 MHz | Adreno 330 @ 450 MHz | Adreno 320 @ 400 MHz |
| Memory | 2 GB dual-channel LPDDR3 @ 933 MHz | 2 GB dual-aqueduct LPDDR3 @ 800 MHz | 2 GB dual-aqueduct LPDDR2 @ 600 MHz |
| Storage | 16/32 GB internal + microSD | sixteen/32 GB internal | 32/64 GB internal |
| Wi-Fi | 802.eleven a/b/yard/northward/ac | 802.eleven a/b/g/n/air-conditioning | 802.eleven a/b/g/n/ac |
| Bluetooth | 4.0 | four.0 | four.0 |
| LTE | Category four | Category 4 | Category three |
| Other | NFC, IR, MHL, GPS | NFC, MHL, GPS | NFC, IR, MHL, GPS |
| Display | 5.0" 1080p LCD | five.0" 1080p LCD | 4.7" 1080p LCD |
| Battery | 9.88 Wh (2,600 mAh) | 8.74 Wh (2,300 mAh) | 8.74 Wh (2,300 mAh) |
| Photographic camera | 4 MP i/iii" sensor with f/2.0 lens + depth sensor | 8 MP i/3.2" sensor with f/2.4 lens, OIS4 | 4 MP 1/iii" sensor with f/2.0 lens, OIS |
Nearly everything has received an upgrade going from the 1 M7 to the One M8, although internal storage in the base model has dropped from 32 GB to 16 GB. This is fabricated up for past the microSDXC card slot, which supports up to 128 GB cards and provides a far cheaper way of getting a lot of storage in the handset.
One downside to the replacement of large internal storage with a microSD card slot is you'll now accept two storage locations in the device, which is a clunky experience on Android. Internal NAND too tends to be faster than microSD carte storage, which makes it a amend selection for app storage. With that said, companies overcharge actress storage options to ridiculous extents, so the microSD slot is more than than welcome.
Before I had easily-on time with the HTC One M8 I was curious to acquire whether the Snapdragon 801 was noticeably faster than the Snapdragon 800 or Snapdragon 600. On paper, the SoC is definitely faster, as you'll discover in the benchmarks below, simply information technology'due south becoming increasingly difficult to tell just how capable it is during regular usage.
The HTC One M8 is undeniably a fast smartphone. Everything from loading apps and browsing the web, to navigating the operating system and multitasking, is ridiculously speedy and very fluid. It definitely appears to have a performance edge over the original HTC One, especially in app loading, only information technology'due south a subtle deviation rather than a wide speed chasm. Comparison the real-globe speed of the HTC 1 M8 to a Snapdragon 800-powered device like the Sony Xperia Z1 Meaty is even trickier, and to exist honest, I tin't really discern which is faster.

Gaming is a slightly different story, as the 578 MHz Adreno 330 GPU is significantly faster than the Snapdragon 600's Adreno 320. The HTC Ane M7 was no slouch in most handheld games, just occasionally the 1080p display would stretch the rendering capabilities of the graphics core. This is no longer the example in the M8: I simply can't find a game on the Play Store that stretches the Adreno 330 in either the Snapdragon 800 or 801 to its absolute limits.
As other publications have noted, the HTC One (M8) is a criterion cheater, which is disappointing but not overly surprising to detect. Out of the benchmarks we perform, 3DMark, GFXBench and Vellamo announced to be affected, with the device artificially boosting the GPU'due south core clock up to the maximum 2.45 GHz when it detects benchmark applications accept launched.
This appears to be slightly unlike behaviour than for the MSM8974AB model, which simply uses a more aggressive governor when benchmarks are detected, rather than forcing the CPU to run at maximum frequencies. Either method is unacceptable, but as most devices contain some form of benchmark cheating code, it evens the playing field somewhat.
Interestingly, HTC will actually make the benchmark adulterous behaviour available in all apps through a setting in the subconscious programmer options. On the Asian review model I received, the 'characteristic' was unfortunately missing.
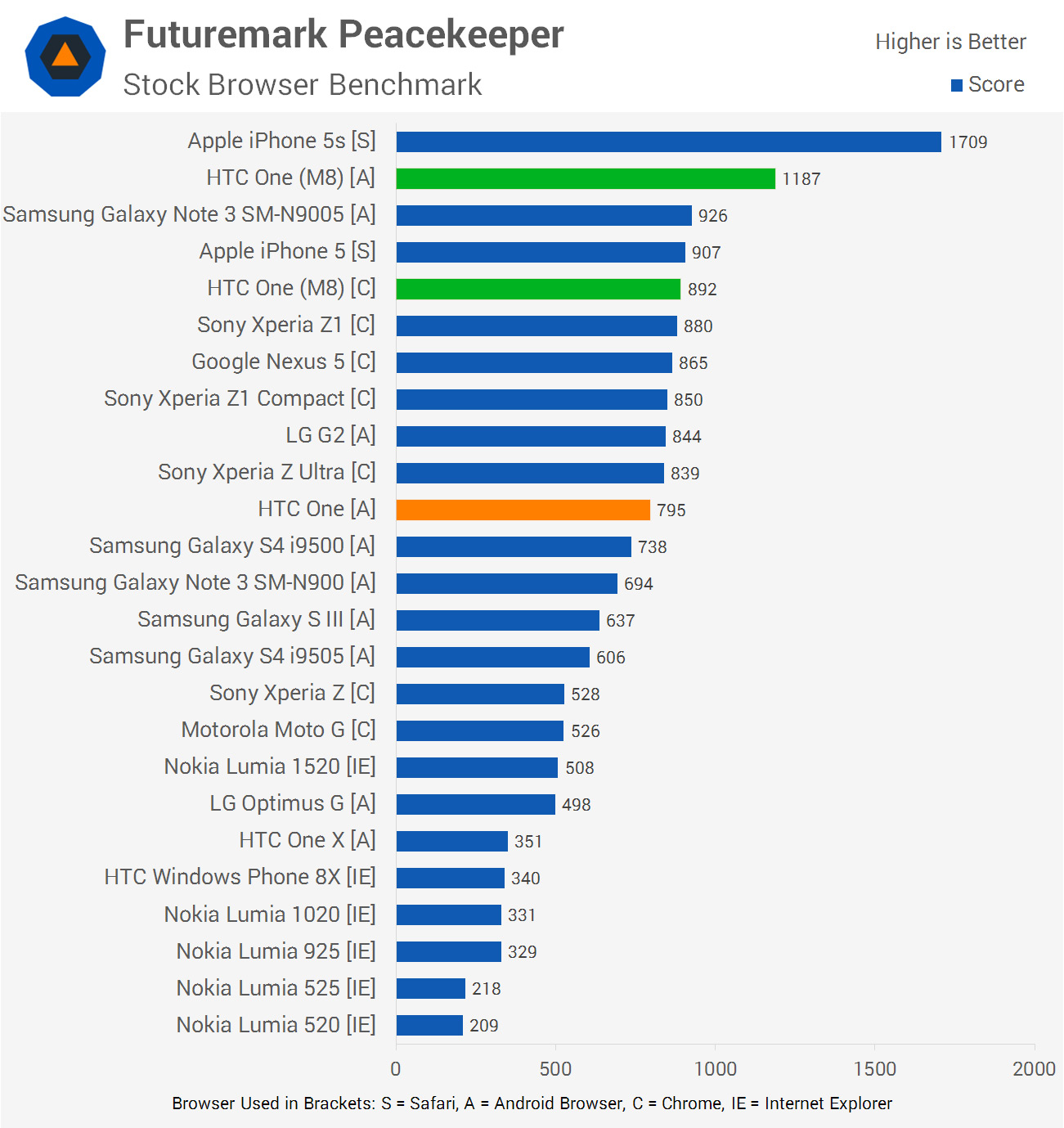
In Peacekeeper, the HTC One (M8) is the new fastest Android device we've tested at TechSpot, falling 30% backside the iPhone 5s, but 28% alee of the next-fastest device: the Snapdragon 800-powered Galaxy Notation 3. The Snapdragon 801 MSM8974AC's clock speed is only 10% higher than the 800, and at that place's xvi% more memory bandwidth, so gains are a little higher than expected. The 1 M8 is 49% faster than the One M7 in this test.

Kraken tells a different story, with the HTC I (M8) performing on-par with the Sony Xperia Z1 in this largely CPU-bound benchmark. Nosotros're too seeing significant performance gains compared to the original HTC 1.


Vellamo'due south HTML5 exam is a curious one, considering it appears the benchmark optimizations have completely failed, and performance has really regressed compared to the HTC One M7. In the Metal test, though, performance is as expected: 3% faster than the Milky way Annotation 3, and 69% faster than the One M7.

In 3DMark we're seeing the One M8's upclocked GPU flex its muscles, topping the charts with a score 12% higher than the Galaxy Annotation three. The GPU is actually clocked 28% college, but I doubt it's running at its maximum frequency throughout the entirety of the criterion's run, especially through the CPU-heavy physics department.


Taking a wait at results for GFXBench and with the Adreno 330 inside, the HTC One M8 is the commencement device with a 1080p display to hit 30 frames per second in the onscreen T-King HD test. Information technology performs 8% faster than the Galaxy Notation 3 offscreen, and xv% faster onscreen thanks to the onscreen buttons reducing the overall rendering resolution.
I've besides included GFXBench'due south new OpenGL ES 3.0 criterion 'Manhattan', which is new in GFXBench 3.0. I've been testing this benchmark with a few devices behind the scenes now, and it's certainly a stressful ane (it refused to load on the Moto G). Like in T-Rex Hd, the One M8 shows that it's the fastest GPU overall in fixed-resolution scenarios, but falls behind in onscreen tests having to return to a near-1080p display.


Another set of benchmarks I've been preparing behind the scenes is a sequential and random read/write test for a smartphone's internal NAND. Here y'all tin really see the differences between the HTC 1 M8 (which tops the charts) and the HTC One M7, the latter of which is much slower beyond the board.

Topping it all off is the USB file transfer test. The HTC 1 M8 is limited to USB 2.0 transfer speeds, so it fails to friction match the Milky way Note 3.
Throughout my usage I had no trouble with Wi-Fi 802.11n on either the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands, Bluetooth 4.0, GPS (which locks chop-chop) or NFC. In that location'southward also the IR LED hidden inside the power button, which can be used to control TVs through the aptly named 'Tv set' app on the handset
Source: https://www.techspot.com/review/801-htc-one-m8/page4.html
Posted by: corsoncludeatic.blogspot.com


0 Response to "HTC One M8 Review > Performance: The Qualcomm Snapdragon 801"
Post a Comment